Create a SLiCAP circuit object
Netlist
SLiCAP accepts SPICE-like netlists as input. Netlists can also be created manually. The SLiCAP syntax slightly deviates from the SPICE syntax; it is described in section Device Models.
Many schematic capture programs can be configured to generate such netlists. SLiCAP comes with symbol libraries for KiCAD, LTspice, gSchem, and Lepton EDA.
Creation of a SLiCAP circuit object from a schematic file or a netlist file is performed with the instruction ‘makeCircuit()`:
# Import the SLiCAP module in its own namespce:
import SLiCAP as sl
# Create and.or initialize a project:
sl.initProject("myProject")
# Create a circuit object (cir) from a schematic or a netlist:
cir = sl.makeCircuit(<path to schematic or netlist>, imgWidth = <number of pixels>)
SLiCAP netlist files will obtain the extension “.cir” and will be placed in the ini.cir_path directory. If a file with extension “.cir” is passed to makeCircuit(), no netlist is generated. In that case the circuit object is created from the existing netlist file.
The netlister is selected from the file extension and the operating system.
File Extension |
MSWindows netlister |
Linux MacOS netlister |
|---|---|---|
.kicad_sch |
KiCAD |
KiCAD |
.asc |
LTspice |
LTspice |
.sch |
gschem gnetlist noqsi |
Lepton EDA gnetlist noqsi |
.cir |
Use exsisting netlist |
Use exsisting netlist |
Drawing size PDF and SVG images are generated only for KiCAD and Lepton EDA schematics.
For a complete description of the function makeCircuit() see makeCircuit.
Below some notes for configuring schematic capture software for working with SLiCAP.
KiCAD
KiCAD is the preferred schematic capture tool for SLiCAP. This is because it works on all platforms and supports generation of PDF and SVG images.
Important
SLiCAP schematics created with KiCAD, should only use symbols from the SLiCAP KiCAD symbol library:
>>> import SLiCAP as sl
>>> sl.ini.kicad_syms
'/home/USER/USER/lib/python3.12/site-packages/SLiCAP/files/kicad/SLiCAP.kicad_sym'
This library must be added to the KiCAD project.
In the KiCAD schematic editor select: Preferences > Manage Symbol Libraries. This will bring up the ‘Symbol Libraries’ Dialog Box.
There you select the tab: “Project Specific Libraries”
Click add “+” to add the library
Enter a Nickname: “SLiCAP” and select the above library path.
Since this library contains all symbols that can be handled by the netlister, it is good practice to deactivate all built-in libraries. This is done in the ‘Global Libraries’ tab of the ‘Symbol Libraries’ Dialog Box.
LTspice
LTspice can be used for netlist generation.
Important
SLiCAP schematics created with LTspice, should only use symbols from the SLiCAP LTspice symbol library:
>>> import SLiCAP as sl
>>> sl.ini.ltspice_syms
'/home/USER/USER/lib/python3.12/site-packages/SLiCAP/files/LTspice/'
This path must be added as LTspice symbol library path.
LTspice works with Windows and Linux (under Wine). A version for MAC is also available. The MAC version of LTspice differs from the windows version and netlist generation from within the SLiCAP (python) environment for this version is not supported. Netlists can also be generated manually.
Go to LTspice for the latest version.
For an overview of SLiCAP symbols for LTspice, please view the LTSpice section.
Configure LTspice for use with SLiCAP
SLiCAP circuits should be made with SLiCAP symbols (and not with the default LTspice symbols). LTspice symbols for SLiCAP are placed in the ~/SLiCAP/LTspice folder.
Start LTspice
On the menu bar click Tools > Control Panel. This will bring up the LTspice control panel:
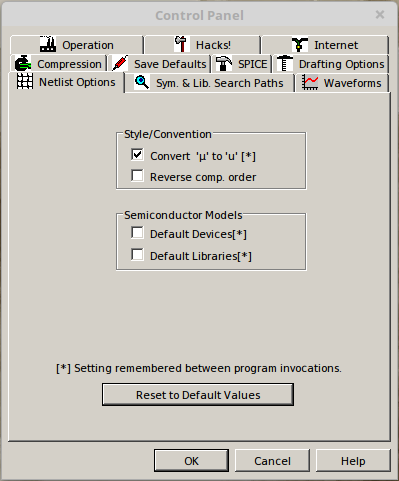
On this control panel select the Netlist Options tab and select the options as shown below:
Then select the
Sym. & Lib. Search Pathstab and enter the full path to ~/SLiCAP/ltspice. This directory contains all the SLiCAP symbol definitions (‘.asy’ files) for LTspice: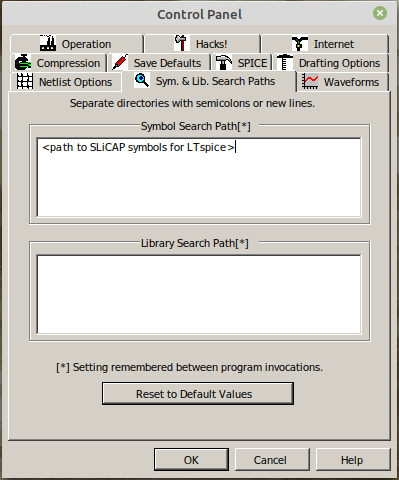
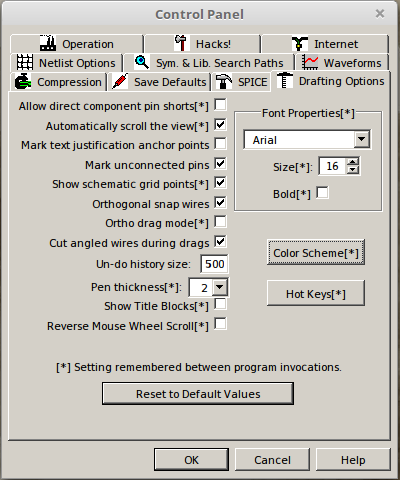
Then select the Drafting Options tab and change the font size and deselect the “Bold” checkbox as shown below. If you want, you can also select different colors for your schematics.
gSchem
The open source gSchem package can also be used in conjunction with SLiCAP. The use of gschem as front-end for SLiCAP has been tested under Linux and Windows. However, for Linux please use Lepton EDA instead.
An MSWindows installer for gschem can be downloaded from: gEDA-20130122.zip. Netlist generation requires the gnet-spice-noqsi spice netlister. SLiCAP has a built-in instruction for netlist generation with gschem and this netlister.
MSWindows installation of gschem is straightforward: simply extract the downloaded gEDA-20130122.zip archive and run the installer. In the drop down menu of the “Select Components” dialog box select “Program only”, for the rest accept default settings.
The netlister is installed by copying ‘gnet-spice-noqsi.scm’ from the downloaded and extracted archive to: “C:Program Files (x86)gEDAgEDAsharegEDAschemegnet-spice-noqsi”.
You need also need to create or modify the file ‘gafrc’ in the ‘~.gEDA' directory. It should have the following content:
(reset-component-library)
(component-library "C:/Program Files (x86)/gEDA/gEDA/share/gEDA/sym/slicap")
Important
SLiCAP schematics created with gSchem, should only use symbols from the SLiCAP gSchem symbol library:
>>> import SLiCAP as sl
>>> sl.ini.ini.gnetlist_syms
'/home/USER/USER/lib/python3.12/site-packages/SLiCAP/files/gSchem/'
Create a folder “C:Program Files (x86)gEDAgEDAsharegEDAsymslicap” and copy the contents of the above the gSchem symbol library to this folder.
If you wish to have a light background you can create or modify the file ‘gschemrc’ in the ‘~.gEDA' directory. Its contents must be:
(load (build-path geda-rc-path "gschem-colormap-lightbg")) ; light background
Be sure you save these two files ‘gafrc’ and ‘gschemrc’ without any file extension.
Lepton-eda
Lepton-eda is a fork of geda-gaf. Please visit https://github.com/lepton-eda/lepton-eda for more information.
For an overview of SLiCAP symbols for lepton-eda, please view the above gSchem section in the help file.
Important
SLiCAP schematics created with lepton-eda, should only use symbols from the SLiCAP lepton-eda symbol library:
>>> import SLiCAP as sl
>>> ini.lepton_eda_syms
'/home/USER/USER/lib/python3.12/site-packages/SLiCAP/files/lepton-eda/'.
This library must be added to lepton-eda.
Create or modify the file: ‘~/.config/lepton-eda/gafrc’ with the contents:
(reset-component-library)
(component-library "<path to SLiCAP symbol Library>" "SLiCAP")
If you wish to have a light background, you can create or modify the file ‘~/.config/lepton-eda/gschemrc’ in your home directory with the contents:
(load (build-path geda-rc-path "gschem-colormap-lightbg")) ; light background
Be sure you save these two files ‘gafrc’ and ‘gschemrc’ without any file extension.
SLiCAP uses the gnet-spice-noqsi spice netlister. It is included in the latest version of lepton-eda.
For compact node names (important for use in symbolic expressions) you need to reconfigure the default net name prefix.
This is how it should be done under Linux:
sudo lepton-cli config --system "netlist" "default-net-name" ""
Display schematics on html pages and in LaTeX reports
Scalable Vector Graphics (“.svg”) images are preferred for displaying on HTML pages, while Portable Document Format (“.pdf”) is preferred for LaTeX reports.
With KiCAD or Lepton-EDA running under Linux or MacOS, drawing-size svg and pdf images will automatically be generated with makeCircuit().
With KiCAD running under Windows, drawing-size svg images will automatically be generated with makeCircuit().
With LTspice you can print schematics to a .PDF file using a PDF printer. Printing and rescaling cannot be invoked by SLiCAP.
With gschem running under MSwindows you can write your schematic file to a .PDF file. Printing and rescaling cannot be invoked by SLiCAP.
When running under MSWindows, you can use pdf2svg-1 or pdf2svg-2 for PDF to SVG conversion. Alternatively, on all platforms, you can use Inkscape instead. If you import PDF files with Inkscape use the import settings Poppler/Cairo import. With this selection, fonts will be converted to Bezier curves.
Inkscape can also be used to resize images from page size to drawing size. This is required for correct display on HTML pages (.svg or .png format) or in LaTeX documents (.pdf format). However, for KiCAD SLiCAP uses built-in scripts for this purpose and Lepton-EDA has such capabilities by default.
With gschem running under Linux or Mac OS you can write your schematic file to a .EPS file.
.EPS files can be converted into .PDF files using the epstopdf command.
Ghostscript is an alternative often available in the package manager of Linux distributions. Otherwise Ghostscript versions can be downloaded from: Ghostscript.